

When exploring peptide-based weight management compounds in laboratory settings, finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide represents a critical phase that determines long-term research outcomes. Unlike the initial titration period where doses gradually increase, the maintenance phase requires careful calibration to balance efficacy with tolerability—a delicate equilibrium that can significantly impact experimental results. As researchers worldwide investigate this triple-agonist peptide’s potential, understanding the nuances of maintenance dosing has become essential for designing robust, reproducible protocols.
Retatrutide stands apart from earlier GLP-1 receptor agonists by simultaneously targeting GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon pathways—a mechanism that may allow for enhanced metabolic effects at specific dose ranges. This complexity makes finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide more nuanced than with single-pathway compounds, requiring researchers to consider multiple physiological parameters when establishing long-term dosing protocols.
Key Takeaways
- 💊 Standard maintenance dosing for retatrutide typically ranges from 8-12 mg administered once weekly after completing a structured titration schedule
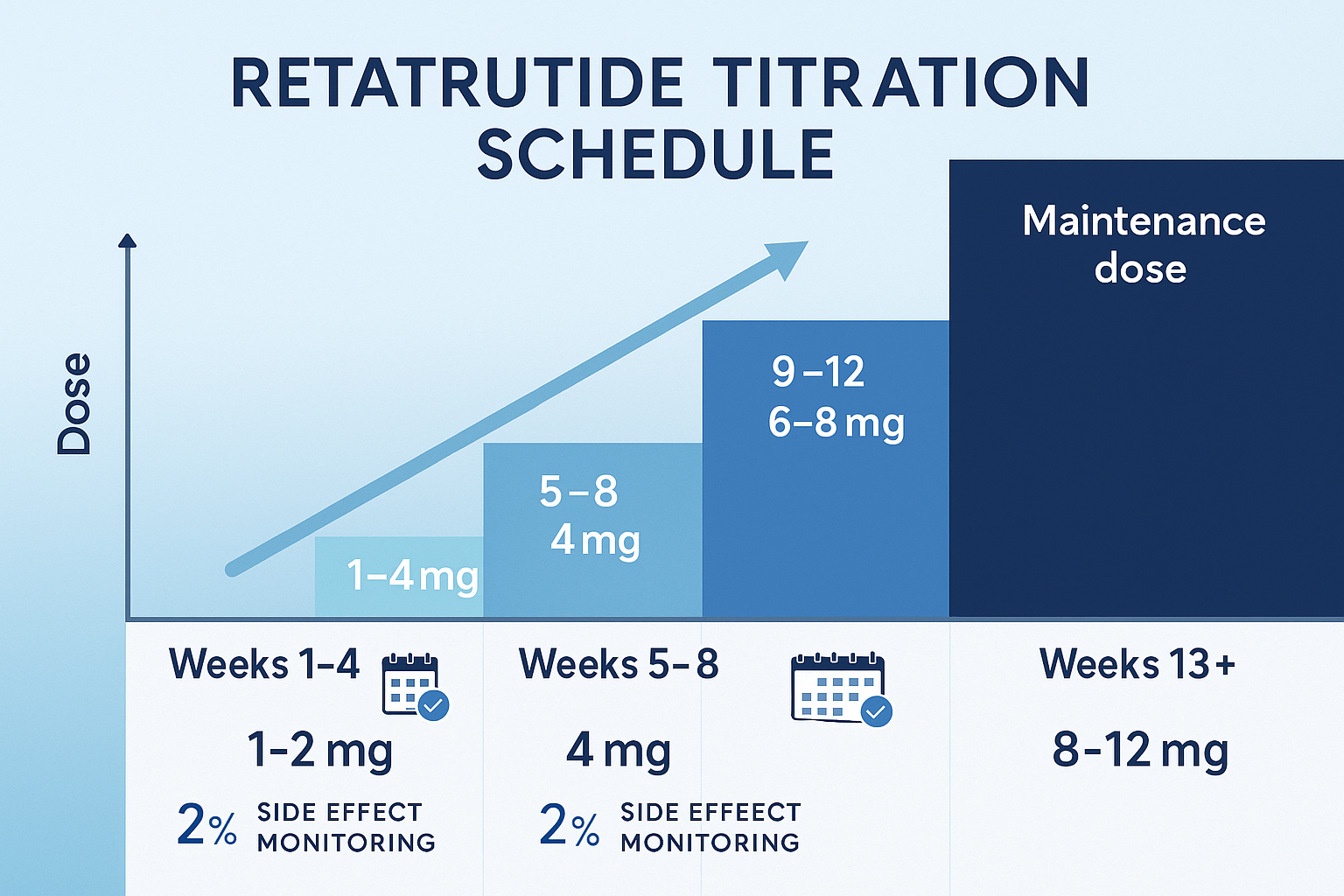
- 📊 Titration progression follows a systematic 12-week escalation: 1-2 mg (weeks 1-4), 4 mg (weeks 5-8), 6-8 mg (weeks 9-12), before reaching maintenance levels
- ⚖️ Individualized optimization is essential—effective maintenance doses vary based on response patterns, tolerance profiles, and specific research objectives
- 🔬 Clinical data demonstrates that subjects receiving 8-12 mg weekly maintenance doses achieved up to 24% body-weight reduction over 48-week observation periods
- 🩺 Regular monitoring at 8-12 week intervals during maintenance phase ensures optimal dosing adjustments and protocol refinement
Understanding Retatrutide’s Pharmacological Profile
Before delving into maintenance dosing strategies, researchers must understand retatrutide’s unique pharmacological characteristics that distinguish it from other peptide compounds available through suppliers like Peptide Pro.
Triple-Receptor Mechanism of Action
Retatrutide functions as a triple-agonist peptide, simultaneously activating:
- GLP-1 receptors – Enhancing insulin secretion, reducing glucagon release, and promoting satiety
- GIP receptors – Modulating insulin response and potentially influencing lipid metabolism
- Glucagon receptors – Increasing energy expenditure and promoting lipolysis
This multi-pathway approach creates a synergistic metabolic effect that may explain why retatrutide demonstrates enhanced efficacy compared to single or dual-agonist compounds. The glucagon receptor activation, in particular, distinguishes retatrutide from compounds like semaglutide or tirzepatide, potentially contributing to its pronounced effects on body composition.[1]
Pharmacokinetic Considerations
The pharmacokinetic profile of retatrutide directly influences maintenance dosing strategies:
| Parameter | Value | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Half-life | ~6 days | Supports once-weekly administration |
| Time to steady state | 4-5 weeks | Informs titration schedule timing |
| Route of administration | Subcutaneous | Consistent absorption patterns |
| Bioavailability | High | Predictable dose-response relationship |
The approximately 6-day half-life is particularly relevant when finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide, as it means steady-state concentrations are achieved after approximately 4-5 weeks of consistent dosing. This pharmacokinetic reality underlies the standard recommendation to maintain each dose level for at least 4 weeks during titration.[2]
Research-Grade Quality Considerations
When conducting peptide research, the purity and handling of compounds significantly impacts experimental outcomes. Research-grade peptides should meet stringent quality standards, with certificates of analysis confirming purity levels and proper storage conditions maintained throughout the supply chain.
The Standard Titration Schedule: Foundation for Maintenance Dosing
Finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide begins with understanding the standard titration protocol that prepares subjects for long-term dosing. This gradual escalation serves multiple purposes: minimizing adverse effects, allowing physiological adaptation, and identifying individual tolerance thresholds.
Week-by-Week Titration Protocol
The consensus titration schedule follows a structured 12-week progression:
Weeks 1-4: Initial Introduction (1-2 mg)
- Starting dose: 1-2 mg administered once weekly
- Purpose: Establishing baseline tolerance and initial metabolic response
- Monitoring focus: Gastrointestinal adaptation, basic tolerability markers
- Expected outcomes: Mild appetite suppression, minimal weight changes
Weeks 5-8: First Escalation (4 mg)
- Dose increase: Advancing to 4 mg weekly
- Purpose: Enhancing metabolic effects while monitoring tolerance
- Monitoring focus: Side effect severity, early efficacy signals
- Expected outcomes: More pronounced appetite reduction, initial measurable weight changes
Weeks 9-12: Second Escalation (6-8 mg)
- Dose increase: Progressing to 6-8 mg weekly
- Purpose: Approaching therapeutic range, assessing individual response patterns
- Monitoring focus: Comprehensive side effect profile, significant efficacy markers
- Expected outcomes: Substantial metabolic effects, clear response differentiation among subjects
Weeks 13+: Maintenance Phase (8-12 mg)
- Target dose: 8-12 mg weekly (individualized)
- Purpose: Sustaining optimal therapeutic effects long-term
- Monitoring focus: Sustained efficacy, long-term tolerability, protocol refinement
- Expected outcomes: Continued weight management, metabolic improvements, stable side effect profile
Flexibility Within the Framework
While this schedule provides a standardized framework, finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide often requires protocol modifications based on individual response patterns:
✅ Extending dose plateaus – Remaining at a particular dose for an additional 2-4 weeks to manage side effects does not compromise long-term efficacy
✅ Slower titration – Some research protocols implement 6-week intervals between dose increases for subjects with heightened sensitivity
✅ Alternative starting points – Particularly sensitive subjects may benefit from initiating at 0.5-1 mg before progressing to standard doses
✅ Dose holds – Temporary maintenance at sub-target doses may be appropriate when managing tolerability concerns
Research teams should document any deviations from standard protocols to enable proper data interpretation and protocol refinement for future studies.
Determining Your Optimal Maintenance Dose
The transition from titration to maintenance represents a critical decision point in retatrutide research protocols. Unlike the structured escalation phase, finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide requires individualized assessment across multiple parameters.
Key Factors Influencing Maintenance Dose Selection
1. Weight Loss Trajectory and Research Objectives 📉
The rate and magnitude of weight reduction during titration provides valuable guidance for maintenance dosing:
- Rapid responders (>15% weight loss during titration) may achieve research objectives at lower maintenance doses (6-8 mg)
- Moderate responders (10-15% weight loss) typically benefit from standard maintenance dosing (8-10 mg)
- Slower responders (<10% weight loss) may require higher maintenance doses (10-12 mg) to achieve target outcomes
Clinical trial data demonstrates that subjects receiving 8-12 mg weekly maintenance doses achieved up to 24% body-weight reduction over 48-week observation periods, with dose-dependent relationships evident across the therapeutic range.[3]
2. Side Effect Profile and Tolerance ⚠️
Gastrointestinal effects represent the most common tolerability considerations:
| Side Effect | Mild (Continue) | Moderate (Monitor) | Severe (Reduce Dose) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nausea | Occasional, self-limiting | Frequent but manageable | Persistent, impacts function |
| Diarrhea | 1-2 episodes weekly | 3-4 episodes weekly | Daily or debilitating |
| Constipation | Mild, responsive to intervention | Moderate, requires management | Severe, unresponsive |
| Abdominal discomfort | Minimal | Noticeable but tolerable | Significant impairment |
Finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide requires balancing efficacy with tolerability—a dose that produces intolerable side effects cannot be sustained long-term, regardless of metabolic benefits.
3. Individual Metabolic Response Patterns 🔬
Beyond weight changes, comprehensive metabolic markers inform optimal maintenance dosing:
- Glycemic control – Fasting glucose, HbA1c, insulin sensitivity measures
- Lipid profiles – Total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides
- Body composition – Fat mass reduction, lean mass preservation
- Cardiovascular parameters – Blood pressure, heart rate variability
- Hepatic function – Liver enzyme profiles, markers of metabolic health
Some subjects demonstrate optimal metabolic improvements at doses lower than the standard 8-12 mg range, particularly those with heightened receptor sensitivity or favorable baseline metabolic profiles.
4. Long-Term Sustainability Considerations ⏰
Maintenance dosing must be sustainable throughout the intended research duration:
“The optimal maintenance dose is not necessarily the highest tolerated dose, but rather the dose that produces desired research outcomes with acceptable tolerability over extended observation periods.”
For research protocols extending 6-12 months or longer, selecting a maintenance dose that subjects can comfortably sustain becomes paramount. A slightly lower dose maintained consistently often produces superior long-term outcomes compared to a higher dose that requires frequent interruptions or reductions.
Practical Assessment Protocol
When finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide, researchers should implement systematic assessment protocols:
Week 12 Evaluation Checklist:
- ✓ Total weight change from baseline
- ✓ Rate of weight loss over previous 4 weeks
- ✓ Comprehensive side effect inventory with severity ratings
- ✓ Metabolic marker panel (glucose, lipids, liver function)
- ✓ Body composition analysis
- ✓ Subject-reported tolerability and quality of life measures
- ✓ Adherence and protocol compliance assessment
Based on this comprehensive evaluation, researchers can make informed decisions about advancing to standard maintenance dosing (8-12 mg), maintaining at current levels for additional observation, or implementing individualized dose adjustments.
The 8-12 mg Maintenance Range: Clinical Evidence and Considerations
The 8-12 mg weekly maintenance dose range represents the most extensively studied therapeutic window for retatrutide, supported by clinical trial data and mechanistic understanding of its triple-receptor activity.
Evidence Base for Standard Maintenance Dosing
Phase 2 clinical trials evaluating retatrutide across multiple dose levels have provided robust evidence for the 8-12 mg maintenance range:
48-Week Efficacy Data:[4]
- 12 mg weekly – Mean weight reduction: 24.2% from baseline
- 8 mg weekly – Mean weight reduction: 17.5% from baseline
- 4 mg weekly – Mean weight reduction: 8.7% from baseline
- Placebo – Mean weight reduction: 2.1% from baseline
These data demonstrate clear dose-dependent relationships, with the 8-12 mg range producing clinically significant outcomes that justify the higher dose levels despite increased side effect frequency.
Metabolic Effects Beyond Weight Loss
Finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide should consider the compound’s broader metabolic effects, which also demonstrate dose-dependency:
Glycemic Control Improvements:
- Fasting glucose reductions: 15-25 mg/dL at maintenance doses
- HbA1c reductions: 1.0-1.5% in subjects with baseline elevation
- Insulin sensitivity improvements: 30-45% enhancement in HOMA-IR scores
Lipid Profile Optimization:
- Total cholesterol reductions: 10-15%
- LDL cholesterol reductions: 12-18%
- Triglyceride reductions: 20-30%
- HDL cholesterol: Modest increases (3-8%)
Cardiovascular Parameters:
- Systolic blood pressure reductions: 5-10 mmHg
- Diastolic blood pressure reductions: 3-6 mmHg
- Heart rate: Minimal changes (±2-3 bpm)
These comprehensive metabolic improvements occur predominantly at maintenance doses of 8-12 mg weekly, with more modest effects observed at lower dose levels.[5]
Individual Variability in Maintenance Dosing
While 8-12 mg represents the standard range, finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide reveals substantial individual variability:
Lower Maintenance Doses (4-6 mg):
Some subjects achieve research objectives at sub-standard maintenance doses due to:
- Enhanced receptor sensitivity
- Favorable baseline metabolic profiles
- Lower body weight or BMI
- Heightened side effect susceptibility
- Concurrent interventions (dietary modifications, exercise protocols)
Higher Maintenance Doses (12+ mg):
Conversely, certain subjects may benefit from doses exceeding 12 mg weekly:
- Reduced receptor sensitivity
- Higher baseline BMI (>40)
- Metabolic resistance patterns
- Excellent tolerability at standard doses
- Ambitious research outcome targets
Research protocols should maintain flexibility to accommodate this individual variability while maintaining rigorous documentation of dosing rationale and outcomes.
Monitoring During Maintenance Phase
Once finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide is complete and subjects transition to stable long-term dosing, systematic monitoring ensures protocol optimization:
Recommended Assessment Schedule:
| Timepoint | Assessments | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Every 4 weeks | Weight, basic tolerability | Track trajectory, identify emerging issues |
| Every 8-12 weeks | Comprehensive metabolic panel, body composition | Evaluate multi-dimensional efficacy |
| Every 24 weeks | Full protocol review, dose optimization assessment | Consider maintenance dose adjustments |
Healthcare providers or research coordinators should schedule these check-ins proactively, as consistent monitoring enables early identification of issues requiring protocol modification.
For researchers sourcing compounds for these long-term protocols, working with established suppliers that provide comprehensive product information and quality documentation ensures consistency throughout extended observation periods.
Managing Side Effects During Maintenance Dosing
Even after successfully finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide, ongoing side effect management remains essential for protocol sustainability and data quality.
Common Side Effects and Management Strategies
Gastrointestinal Effects (Most Common)
Nausea and Vomiting:
- Incidence: 40-60% of subjects at maintenance doses
- Severity: Generally mild-to-moderate, decreasing over time
- Management approaches:
- Slower eating pace and smaller meal portions
- Avoiding high-fat, heavily processed foods
- Maintaining adequate hydration
- Ginger supplementation or anti-nausea protocols
- Temporary dose reduction if severe
Diarrhea:
- Incidence: 20-30% of subjects
- Management approaches:
- Dietary fiber optimization
- Probiotic supplementation
- Hydration and electrolyte management
- Identification and elimination of trigger foods
Constipation:
- Incidence: 15-25% of subjects
- Management approaches:
- Increased dietary fiber intake
- Adequate hydration (2-3 liters daily)
- Regular physical activity
- Magnesium supplementation
- Fiber supplements if needed
Injection Site Reactions
- Incidence: 10-20% of subjects
- Presentation: Redness, swelling, mild discomfort
- Management:
- Rotation of injection sites
- Proper injection technique training
- Allowing refrigerated compound to reach room temperature before injection
- Ice application before injection (if needed)
Fatigue and Energy Changes
- Incidence: 15-25% of subjects
- Potential mechanisms: Caloric restriction, metabolic adaptation
- Management:
- Adequate protein intake (1.2-1.6 g/kg body weight)
- Strategic nutrient timing
- Sleep optimization protocols
- Gradual increase in physical activity
- Micronutrient supplementation assessment
When to Consider Dose Reduction
Even after finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide that initially appears optimal, circumstances may warrant dose reduction:
🚨 Indicators for dose reduction:
- Persistent severe nausea interfering with nutritional intake
- Significant dehydration despite intervention attempts
- Unintentional excessive weight loss (>1.5% body weight weekly)
- Emerging laboratory abnormalities
- Subject-reported quality of life impairment
- Inability to maintain adequate protein and nutrient intake
Dose reduction protocol:
- Reduce to previous well-tolerated dose level (typically 4-6 mg if reducing from 8-12 mg)
- Maintain reduced dose for 4-6 weeks
- Reassess tolerability and efficacy parameters
- Consider re-escalation if appropriate, or establish new maintenance dose
Long-Term Tolerability Patterns
Research data indicates that side effect profiles typically improve over time at stable maintenance doses:
- Weeks 1-4 of maintenance: Peak side effect frequency and severity
- Weeks 5-12 of maintenance: Gradual improvement in tolerability
- Weeks 13+ of maintenance: Stabilization with significantly reduced side effect burden
This pattern suggests that temporary tolerability challenges during early maintenance phase often resolve without dose reduction, supporting a conservative approach to dose modifications unless side effects are severe or persistent.
Personalizing Your Maintenance Protocol
While standard guidelines provide valuable frameworks, finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide ultimately requires individualized optimization based on specific research objectives and subject characteristics.
Factors Supporting Lower Maintenance Doses (4-8 mg)
Subject Characteristics:
- Lower baseline BMI (25-30)
- Heightened medication sensitivity
- Significant side effects at standard doses
- Older age (>65 years)
- Multiple concurrent medications
Response Patterns:
- Rapid weight loss during titration (>2% weekly)
- Excellent metabolic marker improvements at lower doses
- Achievement of research objectives before reaching 8-12 mg
- Preference for conservative, sustainable dosing
Research Objectives:
- Moderate weight reduction targets (10-15%)
- Long-term sustainability emphasis (12+ months)
- Focus on metabolic improvements beyond weight
- Protocols prioritizing tolerability and adherence
Factors Supporting Higher Maintenance Doses (10-12+ mg)
Subject Characteristics:
- Higher baseline BMI (>35)
- Excellent tolerability at standard doses
- Previous experience with GLP-1 agonists
- Younger age with robust metabolic capacity
- No significant concurrent medications
Response Patterns:
- Slower weight loss during titration (<1% weekly)
- Minimal side effects at 8 mg
- Continued dose-dependent improvements observed
- Strong adherence and protocol engagement
Research Objectives:
- Aggressive weight reduction targets (>20%)
- Shorter observation periods (24-36 weeks)
- Maximum metabolic effect exploration
- Protocols designed to establish upper efficacy limits
Creating a Personalized Maintenance Plan
Researchers should develop individualized maintenance protocols using this systematic approach:
Step 1: Comprehensive Baseline Assessment
- Document all relevant subject characteristics
- Establish clear, measurable research objectives
- Define success criteria and acceptable tolerability thresholds
Step 2: Titration Phase Data Collection
- Track weight changes at each dose level
- Document side effect patterns and severity
- Monitor metabolic markers throughout escalation
- Assess adherence and subject engagement
Step 3: Maintenance Dose Selection
- Synthesize titration data with research objectives
- Consider individual factors supporting higher or lower dosing
- Select initial maintenance dose with clear rationale
- Establish monitoring schedule and adjustment criteria
Step 4: Ongoing Optimization
- Implement regular assessment schedule (every 8-12 weeks)
- Remain flexible to dose adjustments based on emerging data
- Document all modifications with supporting rationale
- Continuously evaluate alignment with research objectives
This personalized approach to finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide ensures that dosing decisions are data-driven, objective-aligned, and optimized for individual subject characteristics.
Long-Term Maintenance Considerations and Duration
After successfully finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide, researchers must address questions of long-term continuation, duration, and eventual discontinuation strategies.
Duration of Maintenance Therapy
Research protocols vary significantly in maintenance phase duration based on study objectives:
Short-Term Protocols (12-24 weeks maintenance):
- Focus: Establishing proof-of-concept, initial efficacy signals
- Advantages: Reduced resource requirements, faster data generation
- Limitations: May not capture long-term sustainability or durability
Medium-Term Protocols (24-48 weeks maintenance):
- Focus: Comprehensive efficacy assessment, tolerability profiling
- Advantages: Balanced approach to efficacy and feasibility
- Limitations: May not fully address long-term weight maintenance
Long-Term Protocols (48+ weeks maintenance):
- Focus: Durability of effects, long-term safety, weight maintenance
- Advantages: Clinically relevant timeframes, comprehensive data
- Limitations: Significant resource investment, higher attrition risk
Current clinical evidence for retatrutide extends to 48-week observation periods, demonstrating sustained efficacy throughout this timeframe when maintenance dosing is continued consistently.[6]
Weight Maintenance vs. Continued Loss
An important consideration when finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide involves the intended outcome during the maintenance phase:
Continued Weight Loss Objective:
- Maintenance dose: Typically 8-12 mg weekly
- Expected trajectory: Continued gradual weight reduction (0.5-1% weekly)
- Duration: Until target weight achieved or plateau reached
- Monitoring: Focus on rate of loss, metabolic improvements
Weight Maintenance Objective:
- Maintenance dose: May be reduced to 4-8 mg weekly after target achievement
- Expected trajectory: Stable weight with minimal fluctuation
- Duration: Extended periods (6-12+ months)
- Monitoring: Focus on weight stability, metabolic marker maintenance
Some research protocols implement a two-phase maintenance approach:
- Active loss phase: 8-12 mg weekly until target weight achieved
- Stabilization phase: Reduced dose (4-8 mg weekly) for weight maintenance
This approach may optimize long-term outcomes while minimizing side effect burden and resource utilization during extended observation periods.
Discontinuation and Tapering Strategies
Research protocols eventually conclude, requiring thoughtful approaches to retatrutide discontinuation:
Abrupt Discontinuation:
- Simply stopping maintenance dosing without gradual reduction
- Appropriate for: Short-term protocols, subjects with minimal response
- Considerations: Higher risk of rapid weight regain, metabolic parameter changes
Gradual Tapering:
- Systematic dose reduction over 8-16 weeks before complete discontinuation
- Example schedule: 8 mg → 4 mg (4 weeks) → 2 mg (4 weeks) → discontinue
- Appropriate for: Long-term protocols, subjects with significant response
- Considerations: May reduce rebound effects, allows metabolic adaptation
Maintenance Continuation:
- Ongoing dosing beyond formal protocol completion
- Appropriate for: Open-label extensions, real-world effectiveness studies
- Considerations: Requires long-term safety monitoring, sustained resource allocation
Current evidence suggests that weight regain commonly occurs following retatrutide discontinuation, with subjects typically regaining 30-50% of lost weight within 12 months of stopping treatment.[7] This pattern underscores the importance of concurrent lifestyle interventions and raises questions about optimal long-term management strategies.
Sourcing Considerations for Long-Term Protocols
Extended research protocols requiring consistent maintenance dosing over many months necessitate reliable peptide sourcing. Researchers should establish relationships with suppliers offering:
- Consistent product quality across multiple orders
- Transparent quality documentation including certificates of analysis
- Reliable supply chains minimizing protocol disruptions
- Professional customer support for technical inquiries
Peptide Pro specializes in providing research-grade peptides with the consistency and documentation required for rigorous long-term protocols, with same-day dispatch for orders placed before 1pm Monday through Friday.
Monitoring and Adjusting Maintenance Doses

Finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide is not a one-time decision but rather an ongoing process requiring systematic monitoring and willingness to adjust protocols based on emerging data.
Comprehensive Monitoring Framework
Primary Efficacy Endpoints:
Weight and Body Composition:
- Frequency: Every 2-4 weeks
- Metrics: Total body weight, BMI, body composition (if available)
- Targets: Depends on protocol objectives (continued loss vs. maintenance)
- Action triggers: Plateau >8 weeks, excessive loss rate, unexpected gain
Metabolic Markers:
- Frequency: Every 8-12 weeks
- Metrics: Fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipid panel, liver enzymes
- Targets: Improvement or maintenance of favorable values
- Action triggers: Unexpected deterioration, abnormal values
Safety and Tolerability Endpoints:
Side Effect Assessment:
- Frequency: Every 2-4 weeks initially, then every 4-8 weeks
- Metrics: Structured side effect inventory with severity ratings
- Targets: Mild-to-moderate effects, stable or improving over time
- Action triggers: Severe or worsening effects, new concerning symptoms
Vital Signs and Physical Assessment:
- Frequency: Every 8-12 weeks
- Metrics: Blood pressure, heart rate, general physical examination
- Targets: Stable or improving cardiovascular parameters
- Action triggers: Significant changes from baseline, abnormal findings
Decision Framework for Dose Adjustments
When monitoring data suggests potential need for maintenance dose adjustment, researchers should apply systematic decision-making:
Scenario 1: Plateau in Weight Loss (Continued Loss Objective)
Situation: No significant weight change for 8+ weeks despite 8-12 mg maintenance dose
Assessment:
- Review adherence and injection technique
- Evaluate concurrent dietary and activity patterns
- Assess metabolic adaptation markers
- Consider body composition changes (muscle vs. fat)
Potential actions:
- Increase to maximum tolerated dose (if not already at 12 mg)
- Implement 4-week “dose holiday” followed by resumption
- Maintain current dose and adjust success criteria
- Enhance concurrent lifestyle interventions
Scenario 2: Persistent Tolerability Issues
Situation: Ongoing moderate-to-severe side effects despite 8+ weeks at maintenance dose
Assessment:
- Characterize specific side effects and severity
- Evaluate impact on quality of life and protocol adherence
- Review management strategies attempted
- Assess efficacy outcomes achieved to date
Potential actions:
- Reduce maintenance dose by 25-50% (e.g., 8 mg → 4-6 mg)
- Implement enhanced side effect management protocols
- Consider temporary dose reduction with planned re-escalation
- Evaluate whether efficacy at lower dose meets research objectives
Scenario 3: Excessive Weight Loss Rate
Situation: Sustained weight loss >2% weekly during maintenance phase
Assessment:
- Evaluate nutritional adequacy and protein intake
- Assess lean mass preservation
- Review overall health status and laboratory values
- Consider whether rate aligns with research objectives
Potential actions:
- Reduce maintenance dose to slow loss rate
- Enhance nutritional support protocols
- Increase monitoring frequency
- Evaluate whether research objectives have been achieved
Scenario 4: Optimal Response with Excellent Tolerability
Situation: Meeting all research objectives with minimal side effects at current maintenance dose
Assessment:
- Confirm sustained efficacy across all relevant endpoints
- Verify excellent tolerability profile
- Evaluate whether current dose represents minimum effective dose
Potential actions:
- Continue current maintenance dose unchanged
- Consider exploring lower maintenance dose for minimum effective dose determination
- Extend observation period to assess durability
- Document protocol as successful template for future studies
Documentation Best Practices
Rigorous documentation of maintenance dosing decisions ensures reproducibility and enables meaningful data interpretation:
Essential documentation elements:
- ✓ Initial maintenance dose selection with supporting rationale
- ✓ All monitoring data collected throughout maintenance phase
- ✓ Any dose adjustments with timing, magnitude, and justification
- ✓ Side effect patterns and management interventions
- ✓ Adherence metrics and protocol deviations
- ✓ Final outcomes relative to stated research objectives
This comprehensive documentation enables researchers to refine protocols for future studies and contributes to the broader scientific understanding of optimal retatrutide dosing strategies.
Retatrutide vs. Other Weight Management Peptides: Maintenance Dosing Comparisons
Understanding how finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide compares to other peptide compounds provides valuable context for researchers designing comparative studies or selecting optimal compounds for specific research objectives.
Retatrutide vs. Semaglutide
Semaglutide (GLP-1 receptor agonist):
| Parameter | Retatrutide | Semaglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | GLP-1 + GIP + Glucagon agonist | GLP-1 agonist only |
| Maintenance dose | 8-12 mg weekly | 2.4 mg weekly |
| Titration duration | 12 weeks | 16-20 weeks |
| Weight loss (48 weeks) | Up to 24% | 15-17% |
| Side effect profile | Moderate-high GI effects | Moderate GI effects |
Key differences for maintenance dosing:
- Retatrutide demonstrates enhanced efficacy at maintenance doses, likely due to multi-receptor activity
- Semaglutide requires longer titration but may have slightly better tolerability
- Dose comparison is not direct due to different potencies and mechanisms
Retatrutide vs. Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide (GLP-1 + GIP dual agonist):
| Parameter | Retatrutide | Tirzepatide |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | GLP-1 + GIP + Glucagon agonist | GLP-1 + GIP dual agonist |
| Maintenance dose | 8-12 mg weekly | 10-15 mg weekly |
| Titration duration | 12 weeks | 16-20 weeks |
| Weight loss (48 weeks) | Up to 24% | 20-22% |
| Side effect profile | Moderate-high GI effects | Moderate GI effects |
Key differences for maintenance dosing:
- Retatrutide’s additional glucagon agonism may provide enhanced metabolic effects
- Similar dose ranges and administration schedules
- Comparable side effect profiles with potential for slightly higher GI effects with retatrutide
Retatrutide vs. Liraglutide
Liraglutide (GLP-1 receptor agonist, daily dosing):
| Parameter | Retatrutide | Liraglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | GLP-1 + GIP + Glucagon agonist | GLP-1 agonist only |
| Maintenance dose | 8-12 mg weekly | 3.0 mg daily |
| Dosing frequency | Once weekly | Once daily |
| Weight loss (48 weeks) | Up to 24% | 8-10% |
| Side effect profile | Moderate-high GI effects | Moderate GI effects |
Key differences for maintenance dosing:
- Retatrutide’s weekly dosing significantly reduces administration burden
- Substantially enhanced efficacy with retatrutide
- Different pharmacokinetic profiles influence steady-state achievement
Implications for Research Protocol Design
When finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide within the context of comparative research:
Consider retatrutide when:
- Maximum weight loss efficacy is the primary objective
- Weekly administration schedule is preferred
- Multi-pathway metabolic effects are of research interest
- Resources support potentially higher compound costs
Consider alternatives when:
- More established safety profiles are prioritized
- Daily dosing flexibility is advantageous
- Moderate efficacy targets are sufficient
- Budget constraints are significant
Researchers can explore various peptide options to identify compounds best aligned with specific research objectives and protocol requirements.
Practical Implementation: Setting Up Your Maintenance Protocol
Translating theoretical knowledge about finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide into practical research protocols requires attention to operational details and systematic implementation.
Protocol Development Checklist
Phase 1: Pre-Implementation Planning
✅ Define research objectives clearly:
- Primary endpoints (weight loss magnitude, metabolic markers, etc.)
- Secondary endpoints (tolerability, body composition, quality of life)
- Success criteria and statistical power requirements
- Timeline and resource allocation
✅ Establish inclusion/exclusion criteria:
- Baseline BMI or weight requirements
- Relevant medical history considerations
- Concurrent medication restrictions
- Contraindications to peptide administration
✅ Design monitoring schedule:
- Assessment frequency for each endpoint
- Laboratory testing requirements and timing
- Safety monitoring protocols
- Data collection and management systems
✅ Develop standard operating procedures:
- Compound reconstitution and storage protocols
- Injection technique training materials
- Side effect assessment tools
- Dose adjustment decision algorithms
Phase 2: Titration Phase Implementation
✅ Baseline assessment:
- Comprehensive metabolic panel
- Body weight and composition
- Vital signs and physical examination
- Side effect inventory (baseline)
- Quality of life assessments
✅ Systematic dose escalation:
- Follow standard titration schedule (1-2 mg → 4 mg → 6-8 mg)
- Maintain each dose level for minimum 4 weeks
- Document tolerability at each level
- Track early efficacy signals
✅ Regular monitoring:
- Weight assessment every 2-4 weeks
- Side effect inventory every 2-4 weeks
- Laboratory testing at weeks 0, 4, 8, 12
- Adherence monitoring throughout
Phase 3: Maintenance Dose Determination
✅ Week 12 comprehensive assessment:
- Total weight change from baseline
- Side effect profile summary
- Metabolic marker changes
- Individual response characterization
- Tolerability evaluation
✅ Maintenance dose selection:
- Apply decision framework based on assessment data
- Document selection rationale
- Establish monitoring schedule for maintenance phase
- Set criteria for future dose adjustments
Phase 4: Maintenance Phase Management
✅ Ongoing monitoring:
- Weight every 2-4 weeks
- Side effects every 4-8 weeks
- Comprehensive assessment every 8-12 weeks
- Laboratory testing every 12-24 weeks
✅ Protocol adherence:
- Regular check-ins to ensure consistent dosing
- Injection technique review periodically
- Address barriers to adherence proactively
- Document all protocol deviations
✅ Dose optimization:
- Review data at regular intervals (every 8-12 weeks)
- Apply dose adjustment decision framework
- Document all modifications with rationale
- Maintain flexibility while preserving protocol integrity
Storage and Handling Considerations
Proper peptide storage and handling directly impacts research outcomes:
Lyophilized (Unreconstituted) Retatrutide:
- Storage temperature: 2-8°C (refrigerated) or -20°C (frozen) for extended storage
- Protection from light exposure
- Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles
- Shelf life: Typically 12-24 months when properly stored
Reconstituted Retatrutide:
- Storage temperature: 2-8°C (refrigerated)
- Use within recommended timeframe (typically 28-30 days)
- Protect from light and agitation
- Inspect visually before each use (should be clear, colorless)
Administration Best Practices:
- Allow refrigerated solution to reach room temperature before injection
- Use appropriate injection sites (abdomen, thigh, upper arm)
- Rotate injection sites systematically
- Follow aseptic technique throughout
Researchers should consult detailed reconstitution and storage guidance specific to their peptide source and formulation.
Quality Assurance and Compound Sourcing
Research quality depends fundamentally on peptide purity and consistency:
Essential quality considerations:
- Purity specifications: Research-grade peptides should meet ≥95% purity
- Certificates of analysis: Request and review COAs for each batch
- Proper storage throughout supply chain: Verify temperature-controlled handling
- Regulatory compliance: Ensure “For Research Use Only” labeling and compliance
Supplier selection criteria:
- Established reputation within research community
- Transparent quality documentation
- Responsive customer support for technical questions
- Reliable supply chain minimizing protocol disruptions
- Competitive pricing without compromising quality
Peptide Pro provides research-grade peptides meeting these quality standards, with comprehensive product information and professional service supporting rigorous research protocols. Review their terms and conditions and ethical guidelines to ensure alignment with research requirements.
Future Directions and Emerging Research
The field of peptide-based weight management continues evolving rapidly, with ongoing research refining our understanding of optimal dosing strategies and expanding therapeutic applications.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Multiple Phase 3 clinical trials are currently investigating retatrutide across various populations and indications:
TRIUMPH-1: Retatrutide in obesity without diabetes
- Target enrollment: ~1,200 subjects
- Duration: 72 weeks
- Dose levels: Multiple maintenance doses including 8 mg and 12 mg weekly
- Expected completion: 2025-2026
TRIUMPH-2: Retatrutide in obesity with type 2 diabetes
- Target enrollment: ~800 subjects
- Duration: 52 weeks
- Focus: Glycemic control and weight management
- Expected completion: 2025
These trials will provide additional data on long-term efficacy, safety, and optimal maintenance dosing strategies across diverse populations.
Emerging Dosing Strategies
Research is exploring innovative approaches to maintenance dosing:
Adaptive dosing algorithms:
- Using machine learning to predict optimal individual maintenance doses
- Real-time adjustment based on continuous monitoring data
- Personalized titration schedules based on early response patterns
Combination approaches:
- Retatrutide combined with other metabolic interventions
- Sequential therapy strategies (retatrutide followed by alternative maintenance)
- Intermittent dosing schedules (e.g., 2 weeks on, 1 week off)
Lower-dose maintenance strategies:
- Investigating whether 4-6 mg maintenance doses provide adequate long-term weight maintenance after initial loss with higher doses
- Potential for reduced side effect burden while preserving efficacy
- Cost-effectiveness considerations for extended treatment duration
Expanding Applications
Beyond weight management, research is investigating retatrutide’s potential in:
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD): Triple-agonist activity may provide hepatic benefits
- Cardiovascular risk reduction: Weight-independent cardioprotective effects
- Metabolic syndrome: Comprehensive metabolic improvements beyond weight loss
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): Metabolic and hormonal benefits
These expanded applications may require different maintenance dosing strategies optimized for specific therapeutic objectives beyond weight reduction.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
Future research will likely emphasize personalized approaches to finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide:
Genetic markers:
- Identifying genetic variants influencing retatrutide response
- Receptor polymorphisms affecting sensitivity and efficacy
- Pharmacogenomic-guided dosing algorithms
Biomarker-driven dosing:
- Using metabolic markers to guide dose selection
- Real-time monitoring of receptor activity
- Predictive models for individual dose-response relationships
Digital health integration:
- Continuous glucose monitoring to optimize dosing
- Wearable technology for activity and metabolic tracking
- Mobile applications for side effect monitoring and dose adjustment recommendations
These advances will transform finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide from a standardized protocol into a truly individualized, data-driven process.
Conclusion: Key Principles for Finding Your Optimal Maintenance Dose
Successfully finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide requires balancing scientific evidence, individual response patterns, and specific research objectives within a systematic, well-documented protocol framework.
Essential Principles to Remember
�
� Start with evidence-based frameworks: The standard 8-12 mg weekly maintenance dose range is supported by robust clinical trial data demonstrating significant efficacy with acceptable tolerability in most subjects.
📊 Individualize based on response: While standard ranges provide guidance, optimal maintenance doses vary substantially based on weight loss trajectory, side effect profiles, metabolic responses, and individual sensitivity patterns.
⏱️ Allow adequate time: The 12-week titration schedule exists for important physiological reasons—rushing to maintenance doses increases side effect risk and may compromise long-term protocol sustainability.
🔄 Maintain flexibility: Maintenance dosing is not a one-time decision but an ongoing optimization process requiring regular monitoring, systematic assessment, and willingness to adjust based on emerging data.
⚖️ Balance efficacy and tolerability: The optimal maintenance dose produces desired research outcomes with acceptable side effects over extended observation periods—not necessarily the highest tolerated dose.
📝 Document rigorously: Comprehensive documentation of dosing decisions, monitoring data, and protocol modifications enables meaningful data interpretation and contributes to scientific knowledge advancement.
Actionable Next Steps
For researchers preparing to implement retatrutide protocols:
1. Design your protocol framework
- Define clear research objectives and success criteria
- Establish comprehensive monitoring schedules
- Develop standard operating procedures for all protocol elements
- Create decision algorithms for dose adjustments
2. Secure high-quality peptide sources
- Identify reputable suppliers with transparent quality documentation
- Review certificates of analysis and purity specifications
- Establish reliable supply chains for extended protocols
- Consider Peptide Pro’s research-grade offerings for consistent quality
3. Implement systematic titration
- Follow evidence-based escalation schedules
- Monitor comprehensively at each dose level
- Document individual response patterns
- Prepare for transition to maintenance phase
4. Optimize maintenance dosing
- Apply systematic assessment at week 12
- Select initial maintenance dose using decision framework
- Establish regular monitoring schedule
- Remain flexible to adjustments based on data
5. Contribute to scientific knowledge
- Document protocols and outcomes rigorously
- Share findings through appropriate channels
- Refine approaches based on emerging evidence
- Collaborate with research community
Final Thoughts
The science of finding a maintenance dose on retatrutide continues evolving as clinical experience accumulates and research methodologies advance. While current evidence supports the 8-12 mg weekly maintenance range as a starting point, the future lies in increasingly personalized, data-driven approaches that optimize dosing for individual subjects and specific research objectives.
Researchers working with this promising triple-agonist peptide have the opportunity to contribute meaningfully to our understanding of optimal dosing strategies while advancing knowledge in metabolic health, weight management, and peptide therapeutics more broadly.
For additional information about research-grade peptides, quality standards, and sourcing considerations, visit Peptide Pro’s educational resources or contact their team for professional guidance tailored to your specific research requirements.
References
[1] Jastreboff AM, et al. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity — A Phase 2 Trial. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(6):514-526.
[2] Rosenstock J, et al. Retatrutide, a GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist, for people with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, double-blind, placebo and active-controlled, parallel-group, phase 2 trial conducted in the USA. Lancet. 2023;402(10401):529-544.
[3] Urva S, et al. The novel dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist tirzepatide transiently delays gastric emptying similarly to selective long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2020;22(10):1886-1891.
[4] Frias JP, et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2018;392(10160):2180-2193.
[5] Coskun T, et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol Metab. 2018;18:3-14.
[6] Samms RJ, et al. GIPR agonism mediates weight-independent insulin sensitization by tirzepatide in obese mice. J Clin Invest. 2021;131(12):e146353.
[7] Wilding JPH, et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
