
When exploring novel peptide compounds for research purposes, understanding proper dosing protocols is fundamental to achieving reliable, reproducible results. What’s the right starting dose for retatrutide? This question sits at the heart of contemporary peptide research, particularly as retatrutide emerges as one of the most promising triple-agonist compounds in metabolic research studies. With clinical trials demonstrating remarkable efficacy—including up to 24% body-weight reduction over 48 weeks—determining the optimal entry point for research protocols has become increasingly critical for laboratories and research institutions worldwide.
The complexity of retatrutide dosing stems from its unique pharmacological profile as a GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor agonist. Unlike single-mechanism compounds, this triple-action approach requires careful titration to balance therapeutic potential against tolerability parameters. Research facilities across the UK and internationally are now establishing standardized protocols, with most evidence pointing toward 1-2 mg weekly as the safest, most evidence-based starting point for initial research phases.
Key Takeaways
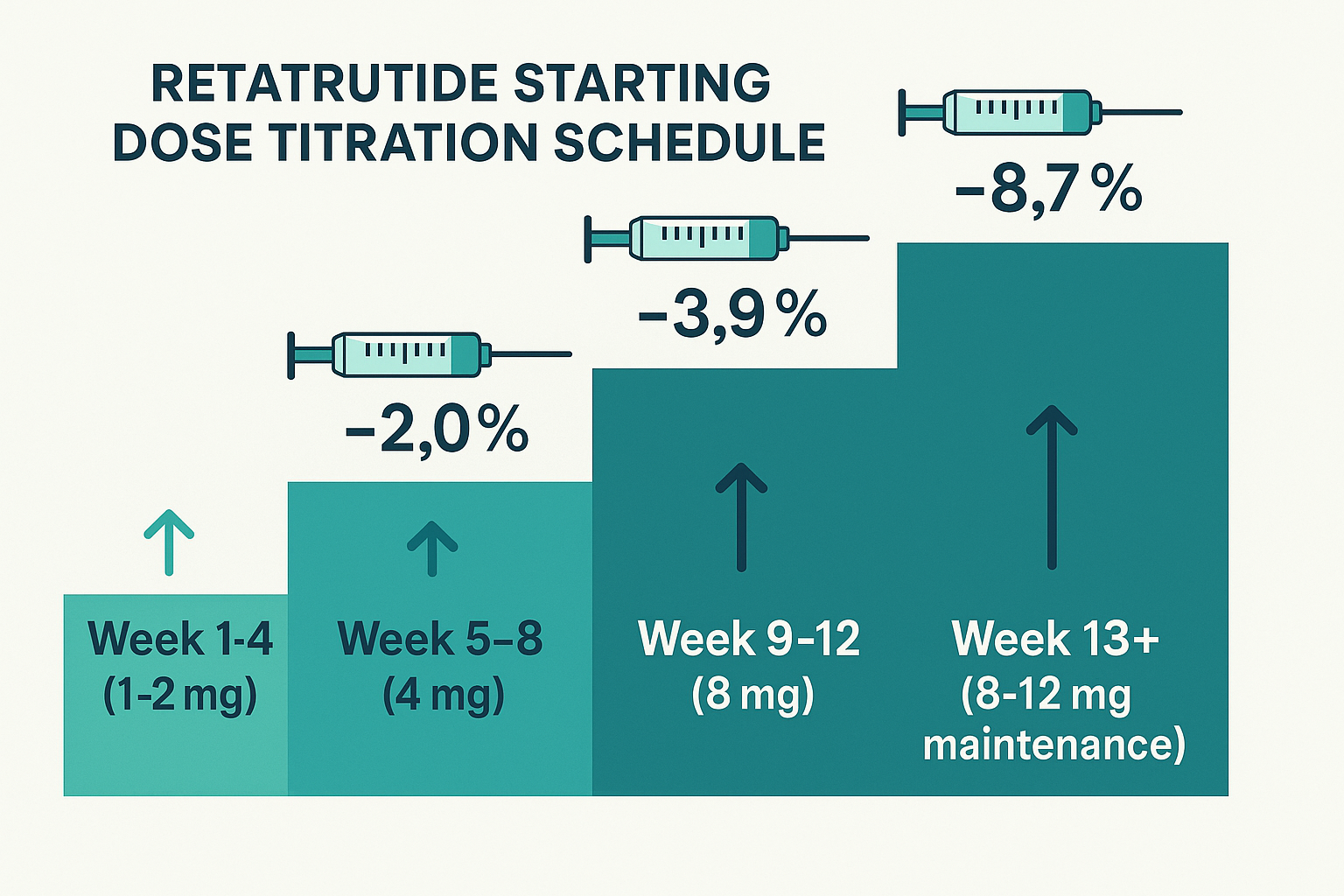
- Standard starting dose: Most research protocols begin with 1-2 mg weekly for the first 2-4 weeks to establish baseline tolerance
- Titration is essential: Gradual dose escalation every 4 weeks (1-2 mg → 4 mg → 8 mg → 8-12 mg maintenance) optimizes outcomes while minimizing adverse reactions
- Individualization matters: Research parameters including subject weight, BMI, metabolic conditions, and tolerance levels should inform dosing decisions
- Lower initial doses reduce side effects: Research shows 2 mg starting doses produce fewer gastrointestinal reactions compared to 4 mg initial protocols
- Maintenance dosing ranges 8-12 mg: Optimal long-term research outcomes typically occur at these levels, though some studies explore up to 16 mg weekly
Understanding Retatrutide: The Triple-Agonist Research Compound
Retatrutide represents a significant advancement in peptide research, functioning as a triple receptor agonist that simultaneously activates GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1), GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide), and glucagon receptors. This multi-targeted mechanism distinguishes it from earlier single or dual-agonist compounds, creating a more comprehensive metabolic effect profile in research models.
Mechanism of Action
The compound’s three-pronged approach works synergistically:
- GLP-1 activation: Enhances insulin secretion, reduces glucagon release, slows gastric emptying, and promotes satiety signals
- GIP activation: Improves insulin sensitivity, supports glucose metabolism, and may influence lipid processing
- Glucagon activation: Increases energy expenditure, promotes fat oxidation, and supports metabolic rate elevation
This combination creates what researchers term a “metabolic reset,” making retatrutide particularly valuable for studies examining weight management, metabolic syndrome, and related conditions. Laboratories sourcing research-grade peptides require exceptional purity standards to ensure consistent results across these complex mechanisms.
Research Applications
Current research protocols utilizing retatrutide focus on several key areas:
- Obesity and weight management studies
- Metabolic syndrome investigation
- Type 2 diabetes research models
- Cardiovascular risk factor analysis
- Long-term metabolic adaptation studies
The compound’s versatility makes it suitable for diverse research contexts, though proper dosing remains critical regardless of the specific application.
What’s the Right Starting Dose for Retatrutide? Evidence-Based Recommendations
Determining the appropriate initial dose for retatrutide research protocols requires careful consideration of multiple factors. Current evidence from clinical trials and research institutions has established clear guidelines that prioritize both efficacy and tolerability.
The 1-2 mg Weekly Standard
Most research protocols begin with 1-2 mg administered once weekly for an initial period of 2-4 weeks. This conservative starting point serves several critical functions:
✅ Establishes baseline tolerance: Allows research subjects to acclimate to the compound’s effects before dose escalation
✅ Minimizes adverse reactions: Lower initial doses significantly reduce gastrointestinal side effects
✅ Provides assessment window: Enables researchers to monitor initial responses and adjust protocols accordingly
✅ Follows evidence-based precedent: Aligns with successful clinical trial methodologies
Research data indicates that starting at 2 mg weekly produces fewer and less severe gastrointestinal effects compared to protocols initiating at 4 mg, making it the preferred entry point for most applications [1].
Alternative Starting Protocols
While 1-2 mg represents the standard, some research facilities may employ alternative starting doses based on specific parameters:
| Starting Dose | Duration | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | 2-4 weeks | Conservative protocols, sensitive populations, initial tolerance testing |
| 2 mg | 2-4 weeks | Standard research protocol, balanced approach |
| 2.5 mg | 2-4 weeks | Accelerated protocols, higher BMI subjects, specific research objectives |
The choice between these options should reflect the specific research objectives, subject characteristics, and institutional protocols. Facilities conducting peptide research can explore various research-grade options to support their specific protocol requirements.
Comparison with Other Compounds
Understanding retatrutide’s starting dose in context with similar compounds provides valuable perspective:
Retatrutide vs. Semaglutide: Semaglutide typically begins at 0.25 mg weekly, significantly lower than retatrutide’s 1-2 mg starting point. This difference reflects retatrutide’s distinct pharmacological profile and potency characteristics.
Retatrutide vs. Tirzepatide: Tirzepatide (a dual GLP-1/GIP agonist) commonly starts at 2.5 mg weekly, slightly higher than retatrutide’s conservative entry point, though both follow similar escalation principles.
These comparisons underscore the importance of compound-specific dosing protocols rather than extrapolating from related peptides.
Eligibility Criteria and Pre-Dosing Assessment
Before initiating any retatrutide research protocol, comprehensive assessment of eligibility criteria ensures appropriate subject selection and optimizes research outcomes. These parameters mirror clinical practice standards while adapting to research-specific requirements.
BMI and Weight Parameters
Research protocols typically establish eligibility thresholds based on body mass index:
- BMI ≥30: Primary eligibility criterion for obesity-focused research
- BMI ≥27 with comorbidities: Alternative threshold when weight-related conditions are present
- Weight-related conditions: May include metabolic syndrome markers, cardiovascular risk factors, or glucose regulation abnormalities
These criteria help ensure research subjects represent appropriate populations for metabolic intervention studies while maintaining safety parameters.
Health Status Considerations
Comprehensive health assessment should evaluate:
🔬 Metabolic markers: Baseline glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, lipid profiles
🔬 Cardiovascular status: Blood pressure, heart rate, cardiovascular risk factors
🔬 Gastrointestinal history: Previous tolerance of similar compounds, existing GI conditions
🔬 Hepatic and renal function: Liver and kidney parameters within acceptable ranges
🔬 Contraindications: Personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma, multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2
This thorough pre-protocol assessment establishes baseline parameters and identifies potential risk factors that might influence dosing decisions.
Personalization Factors
Research protocols should account for individual variability:
- Age considerations: Metabolic responses may vary across age groups
- Sex differences: Hormonal factors can influence compound metabolism and effects
- Concurrent medications: Potential interactions with other compounds or medications
- Previous peptide exposure: Prior experience with GLP-1 agonists or similar compounds
Facilities conducting sophisticated peptide research can access detailed product information and certificates of analysis to support protocol development and regulatory compliance.
The Retatrutide Titration Schedule: Step-by-Step Progression
Proper dose escalation represents one of the most critical aspects of retatrutide research protocols. The standard titration schedule follows a methodical, evidence-based progression that balances efficacy optimization with tolerability management.
Standard 4-Week Escalation Protocol
The most widely adopted titration schedule progresses as follows:
Weeks 1-4: Initial Phase (1-2 mg)
- Establish baseline tolerance
- Monitor for initial adverse reactions
- Assess early metabolic responses
- Collect preliminary efficacy data
Weeks 5-8: First Escalation (4 mg)
- Double the initial dose
- Continue monitoring tolerance parameters
- Evaluate dose-response relationships
- Document any emerging side effects
Weeks 9-12: Second Escalation (8 mg)
- Further dose increase to therapeutic range
- Assess cumulative effects
- Monitor for dose-dependent responses
- Evaluate subject adaptation
Week 13+: Maintenance Phase (8-12 mg)
- Establish optimal long-term dosing
- Some protocols may explore up to 16 mg
- Focus on sustained efficacy assessment
- Long-term tolerability evaluation
Flexible Titration Approaches
While the standard 4-week escalation provides a reliable framework, research protocols may incorporate flexibility based on observed responses:
⏱️ Extended duration at current dose: If significant side effects emerge, maintaining the current dose for an additional 2-4 weeks allows better adaptation without compromising long-term efficacy
⏱️ Accelerated progression: In specific research contexts with well-tolerated initial phases, some protocols may consider shorter intervals, though this approach requires careful justification
⏱️ Dose reduction: If adverse reactions become problematic, stepping back to the previous dose level for an extended period often resolves issues while maintaining research continuity
Why Titration Pace Matters
Research demonstrates that gradual titration significantly reduces the frequency and severity of gastrointestinal side effects—the most common adverse reactions associated with retatrutide and related compounds [2]. The step-wise approach allows:
- Progressive receptor adaptation
- Gradual metabolic adjustments
- Better identification of individual tolerance thresholds
- Reduced protocol discontinuation rates
- More reliable long-term data collection
Importantly, taking longer to reach maintenance doses does not reduce ultimate efficacy. Research subjects who spend additional time at intermediate doses achieve comparable outcomes to those following accelerated schedules, while experiencing fewer adverse events.
Factors Influencing Individual Starting Dose Decisions
While evidence-based guidelines provide a framework, determining what’s the right starting dose for retatrutide in specific research contexts requires consideration of multiple individualized factors. This personalization approach optimizes both safety and scientific outcomes.
Subject-Specific Variables
Body Weight and Composition
- Higher baseline weight may support slightly higher starting doses
- Body composition (lean vs. adipose tissue ratio) influences distribution
- Metabolic rate variations affect compound processing
Metabolic Status
- Insulin sensitivity levels
- Glucose regulation capacity
- Lipid metabolism efficiency
- Previous metabolic intervention responses
Age and Physiological Factors
- Younger subjects may metabolize compounds differently than older populations
- Hormonal status influences receptor sensitivity
- Cardiovascular fitness affects distribution and clearance
Previous Peptide Exposure
Research subjects with prior exposure to similar compounds may demonstrate different tolerance patterns:
- GLP-1 agonist experience: Previous exposure to semaglutide or liraglutide may indicate better initial tolerance
- Dual-agonist familiarity: Prior tirzepatide exposure suggests adaptation to multi-receptor activation
- Naive subjects: First-time exposure typically warrants more conservative starting doses
Research Objectives and Protocol Design
The specific aims of the research project should inform dosing decisions:
�
� Efficacy-focused studies: May employ standard progression to reach therapeutic doses efficiently �
� Tolerability research: Might utilize more conservative starting points and extended titration �
� Dose-response investigations: Require systematic exploration of multiple dose levels �
� Long-term outcome studies: Prioritize sustainable dosing that maintains subject retention
Researchers developing comprehensive protocols can access educational resources covering peptide handling, reconstitution principles, and storage requirements to ensure optimal compound stability throughout extended studies.
Tolerance and Side Effect History
Individual susceptibility to common adverse reactions should guide starting dose selection:
- Gastrointestinal sensitivity: History of nausea, vomiting, or GI distress with medications suggests lower starting doses
- Previous discontinuation: Subjects who discontinued similar compounds due to side effects benefit from more gradual introduction
- Robust tolerance: Subjects with excellent tolerance of related compounds may accommodate standard or slightly higher starting doses
Managing Side Effects Through Proper Dosing
Understanding the relationship between dosing strategy and adverse reaction profiles represents a critical component of successful retatrutide research protocols. Proper dose management significantly influences both subject retention and data quality.
Common Adverse Reactions
Research with retatrutide and related triple-agonist compounds consistently identifies several primary adverse reactions:
Gastrointestinal Effects (Most Common)
- Nausea (frequency: 20-40% depending on dose)
- Vomiting (10-20%)
- Diarrhea (15-25%)
- Constipation (10-15%)
- Abdominal discomfort (15-20%)
Metabolic Effects
- Decreased appetite (very common, often desired in weight research)
- Fatigue (10-15%)
- Dizziness (5-10%)
Injection Site Reactions
- Local redness or irritation (5-10%)
- Mild pain or discomfort (<5%)
Dose-Dependent Relationships
Research clearly demonstrates that starting dose directly correlates with adverse reaction frequency and severity. Studies comparing 2 mg versus 4 mg starting doses show:
- 40% reduction in moderate-to-severe nausea with lower starting dose
- 35% fewer instances of vomiting during initial weeks
- Better protocol adherence and lower discontinuation rates
- Comparable long-term efficacy despite slower initial progression
This data strongly supports conservative starting doses as the optimal approach for most research applications.
Mitigation Strategies
Beyond appropriate starting doses, several strategies help manage adverse reactions:
| Strategy | Implementation | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Slower titration | Extend time at each dose level by 2-4 weeks | High for GI effects |
| Dietary modifications | Smaller, more frequent meals; avoid high-fat foods | Moderate to high |
| Hydration optimization | Increased fluid intake, especially with GI symptoms | Moderate |
| Timing adjustments | Administer at specific times relative to meals | Moderate |
| Temporary dose reduction | Step back to previous tolerated dose | High when needed |
When to Adjust Dosing
Research protocols should establish clear criteria for dose modifications:
Indicators for extending current dose:
- Persistent moderate nausea beyond first week
- Any vomiting episodes
- Significant GI distress affecting daily function
- Subject request for slower progression
Indicators for dose reduction:
- Severe or intolerable adverse reactions
- Multiple concurrent side effects
- Inability to maintain adequate nutrition/hydration
- Safety concerns
Indicators for protocol discontinuation:
- Severe adverse events
- Persistent intolerance despite dose adjustments
- Development of contraindications
- Subject withdrawal of consent
Facilities conducting peptide research should maintain comprehensive safety protocols and documentation procedures to ensure proper adverse event tracking and management.
Administration Protocols and Practical Considerations
Proper administration technique and practical protocol management significantly influence both safety and efficacy outcomes in retatrutide research. Understanding these operational aspects ensures consistent, reliable results.
Subcutaneous Injection Protocol
Retatrutide is administered as a once-weekly subcutaneous injection, consistent with other GLP-1 and GIP agonist compounds. Standard protocols include:
Injection Sites
- Abdomen (most common, excluding 2-inch radius around navel)
- Thigh (anterior and lateral aspects)
- Upper arm (posterior aspect, requires assistance)
- Rotation recommended: Alternating sites reduces local reactions
Injection Technique
- Prepare injection site with appropriate antiseptic
- Pinch skin to create subcutaneous fold
- Insert needle at 45-90° angle (depending on needle length and subject adiposity)
- Inject slowly and steadily
- Withdraw needle and apply gentle pressure
- Dispose of sharps in appropriate containers
Timing Considerations
- Administer on same day each week for consistency
- Time of day may be adjusted based on side effect patterns
- If dose missed, administer within 4 days; if >4 days, skip and resume regular schedule
Reconstitution and Storage
For research-grade lyophilized peptides, proper reconstitution and storage are critical:
Reconstitution Process
- Use bacteriostatic water for multi-dose applications
- Add diluent slowly down vial wall to minimize foaming
- Gently swirl (never shake) to dissolve
- Inspect for particulates or discoloration before use
- Calculate concentration based on final volume
Storage Requirements
- Lyophilized powder: Store at 2-8°C in original packaging, protected from light
- Reconstituted solution: Refrigerate at 2-8°C, use within manufacturer-specified timeframe (typically 28 days)
- Never freeze: Freezing denatures peptide structure
- Transport considerations: Maintain cold chain during shipping
Research facilities can access detailed reconstitution and storage guidance to ensure optimal compound stability and research reliability.
Documentation and Tracking
Comprehensive protocol documentation ensures research integrity:
📋 Dose administration logs: Date, time, dose, injection site, administrator
📋 Adverse event tracking: Type, severity, duration, relationship to dosing
📋 Efficacy measurements: Weight, metabolic markers, protocol-specific outcomes
📋 Protocol deviations: Any variations from standard procedures with justification
📋 Storage conditions: Temperature logs, reconstitution dates, expiration tracking
Maintenance Dosing: Optimizing Long-Term Research Protocols

Once titration is complete, establishing appropriate maintenance dosing becomes the focus for long-term research applications. This phase represents the primary data collection period for most efficacy studies.
Target Maintenance Range
Research protocols typically establish maintenance doses within the 8-12 mg weekly range, though individual optimization may vary:
8 mg weekly
- Lower end of therapeutic range
- Suitable for subjects with excellent response at this level
- May reduce adverse reaction frequency
- Appropriate for long-term tolerability studies
10 mg weekly
- Mid-range therapeutic dose
- Balances efficacy and tolerability
- Common choice for extended protocols
- Well-supported by clinical trial data
12 mg weekly
- Upper standard therapeutic range
- Maximum efficacy for most subjects
- May be necessary for subjects with higher BMI or specific research objectives
- Requires careful tolerability monitoring
Up to 16 mg weekly
- Explored in some research protocols
- Reserved for specific applications
- Requires robust safety monitoring
- Limited long-term data compared to lower doses
Efficacy at Maintenance Doses
Clinical research demonstrates impressive outcomes at optimal maintenance dosing:
- Up to 24% body-weight reduction over 48 weeks in clinical trials [3]
- Sustained metabolic improvements including glucose regulation and lipid profiles
- Dose-dependent responses with higher maintenance doses generally producing greater effects
- Plateau effects typically occurring after 36-48 weeks of treatment
Duration Considerations
Long-term research protocols must consider:
⏰ Minimum effective duration: Most metabolic studies require at least 24 weeks to capture meaningful outcomes
⏰ Optimal assessment window: 48-52 weeks provides comprehensive efficacy and safety data
⏰ Extended protocols: Some research extends to 2+ years to evaluate long-term sustainability
⏰ Washout periods: Post-treatment observation periods assess durability of effects
Maintenance Phase Adjustments
Even during maintenance, dosing may require modification:
Reasons for dose increase:
- Efficacy plateau before achieving research objectives
- Excellent tolerability with room for optimization
- Protocol-specified escalation to maximum dose
Reasons for dose decrease:
- Emerging tolerability issues
- Achievement of target outcomes at lower dose
- Safety considerations
- Subject preference
Researchers maintaining extensive peptide inventories can explore comprehensive product ranges to support diverse protocol requirements and ensure consistent supply throughout long-term studies.
Retatrutide vs. Other Metabolic Peptides: Dosing Comparisons
Understanding retatrutide’s dosing profile in context with related compounds provides valuable perspective for research protocol development and helps explain the rationale behind specific starting dose recommendations.
Retatrutide vs. Semaglutide
Semaglutide (GLP-1 agonist only) follows a distinctly different dosing pattern:
| Parameter | Retatrutide | Semaglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Starting dose | 1-2 mg weekly | 0.25 mg weekly |
| Titration interval | 4 weeks | 4 weeks |
| Typical escalation | 1-2 → 4 → 8 → 8-12 mg | 0.25 → 0.5 → 1.0 → 2.4 mg |
| Maintenance range | 8-12 mg | 1.0-2.4 mg |
| Mechanism | Triple agonist (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon) | Single agonist (GLP-1) |
The substantially higher dosing for retatrutide reflects its broader mechanism and different potency profile, not simply “stronger” effects. The triple-agonist approach requires higher absolute doses to achieve optimal receptor activation across all three pathways.
Retatrutide vs. Tirzepatide
Tirzepatide (dual GLP-1/GIP agonist) provides a closer comparison:
| Parameter | Retatrutide | Tirzepatide |
|---|---|---|
| Starting dose | 1-2 mg weekly | 2.5 mg weekly |
| Titration interval | 4 weeks | 4 weeks |
| Typical escalation | 1-2 → 4 → 8 → 8-12 mg | 2.5 → 5 → 7.5 → 10-15 mg |
| Maintenance range | 8-12 mg | 10-15 mg |
| Mechanism | Triple agonist (GLP-1/GIP/glucagon) | Dual agonist (GLP-1/GIP) |
Retatrutide’s slightly lower starting dose compared to tirzepatide likely reflects the addition of glucagon receptor activation, which requires more careful initial titration to assess tolerability.
Efficacy Comparisons
Research suggests retatrutide may produce superior weight reduction outcomes compared to single or dual agonists:
- Retatrutide: Up to 24% body-weight reduction at 48 weeks
- Tirzepatide: Approximately 15-22% body-weight reduction at 72 weeks (dose-dependent)
- Semaglutide: Approximately 15-17% body-weight reduction at 68 weeks
These differences underscore the potential advantages of the triple-agonist approach, though direct head-to-head comparative studies remain limited.
Implications for Protocol Selection
When designing research protocols, compound selection should consider:
🔬 Research objectives: Triple-agonist mechanisms may be preferable for comprehensive metabolic studies
🔬 Subject population: Different compounds may suit different baseline characteristics
🔬 Tolerability priorities: Single-agonist approaches may offer simpler side effect profiles
🔬 Duration requirements: Long-term studies benefit from compounds with extensive safety data
🔬 Budget considerations: Compound costs and availability vary significantly
Safety Monitoring and Research Best Practices
Comprehensive safety monitoring represents an essential component of responsible retatrutide research protocols. Proper oversight ensures subject wellbeing while maintaining data integrity and regulatory compliance.
Pre-Protocol Assessment
Before initiating retatrutide administration, establish comprehensive baseline parameters:
Laboratory Assessments
- Complete metabolic panel (glucose, electrolytes, kidney function)
- Liver function tests (ALT, AST, bilirubin)
- Lipid profile (total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, triglycerides)
- Hemoglobin A1c (if diabetes-related research)
- Thyroid function (TSH, free T4)
- Complete blood count
Physical Measurements
- Weight and BMI
- Blood pressure and heart rate
- Waist circumference
- Body composition (if protocol-appropriate)
Medical History
- Comprehensive health questionnaire
- Medication and supplement inventory
- Previous peptide or metabolic drug exposure
- Family history of relevant conditions
Ongoing Monitoring Schedule
Regular assessment throughout the protocol ensures early detection of adverse trends:
Weekly (during titration)
- Weight measurement
- Adverse event inquiry
- Injection site examination
- Vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate)
Monthly
- Comprehensive symptom review
- Laboratory monitoring (selected parameters)
- Protocol compliance assessment
- Dose adjustment evaluation
Quarterly
- Full laboratory panel
- Comprehensive physical examination
- Efficacy outcome measurements
- Long-term tolerability assessment
Red Flags and Stopping Criteria
Research protocols should establish clear criteria for dose modification or discontinuation:
⚠️ Immediate discontinuation indicators:
- Severe allergic reactions
- Pancreatitis symptoms (severe abdominal pain, vomiting)
- Significant hepatic dysfunction
- Severe or persistent hypoglycemia
- Thyroid abnormalities suggesting medullary carcinoma
⚠️ Dose reduction indicators:
- Persistent moderate-severe nausea
- Significant weight loss velocity (>2% body weight per week)
- Symptomatic hypotension
- Moderate laboratory abnormalities
⚠️ Extended monitoring indicators:
- Mild-moderate adverse reactions
- Borderline laboratory values
- Subject concerns about tolerability
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Research facilities must maintain rigorous compliance standards:
📜 Institutional protocols: All research must follow institutional review board (IRB) or ethics committee approval
📜 Informed consent: Comprehensive disclosure of risks, benefits, and alternatives
📜 Adverse event reporting: Timely documentation and reporting per regulatory requirements
📜 Data integrity: Accurate, complete, contemporaneous record-keeping
📜 Subject rights: Respect for autonomy, privacy, and right to withdraw
Facilities can review terms and conditions and privacy policies to ensure comprehensive regulatory compliance frameworks.
Sourcing Research-Grade Retatrutide: Quality Considerations
The quality and purity of research peptides directly impacts both safety and scientific validity. Establishing reliable sourcing relationships with reputable suppliers represents a critical component of successful research protocols.
Purity Standards
Research-grade peptides should meet stringent purity specifications:
✓ Minimum purity: ≥98% (HPLC-verified)
✓ Endotoxin levels: <1.0 EU/mg
✓ Sterility: Confirmed through appropriate testing
✓ Identity verification: Mass spectrometry confirmation
✓ Consistency: Batch-to-batch reproducibility
Lower purity compounds may contain contaminants, degradation products, or incorrect sequences that compromise research outcomes and potentially introduce safety risks.
Documentation Requirements
Reputable suppliers provide comprehensive documentation:
- Certificates of Analysis (CoA): Independent third-party verification of purity, identity, and quality
- Storage recommendations: Specific temperature and handling requirements
- Reconstitution guidance: Appropriate diluents and techniques
- Expiration dating: Stability-based shelf life information
- Regulatory compliance: Appropriate labeling (“For Research Use Only”)
Supply Chain Considerations
Reliable research requires consistent peptide availability:
🚚 Inventory management: Ensure suppliers maintain adequate stock levels
🚚 Shipping conditions: Temperature-controlled packaging and expedited delivery options
🚚 Geographic coverage: UK and international shipping capabilities
🚚 Order tracking: Comprehensive logistics visibility
🚚 Customer support: Responsive technical and ordering assistance
PEPTIDE PRO offers same-day dispatch for orders placed before 1pm (Monday-Friday), ensuring minimal delays in research timelines. Fast UK delivery and international shipping options support research facilities worldwide.
Verification and Testing
Research facilities should implement internal quality verification:
- Visual inspection: Check for proper packaging, labeling, and physical appearance
- Documentation review: Verify CoA matches product received
- Storage validation: Confirm appropriate storage conditions upon receipt
- Optional independent testing: Consider periodic third-party verification for critical protocols
Responsible Sourcing
Ethical research requires responsible peptide procurement:
- Legitimate suppliers: Avoid gray-market or unverified sources
- Proper labeling: Ensure “For Research Use Only” designation
- Regulatory compliance: Verify supplier adherence to applicable regulations
- Transparent practices: Work with suppliers who provide complete product information
Researchers can explore comprehensive peptide catalogues from established suppliers committed to purity, transparency, and professional service.
Future Directions: Retatrutide Research in 2025 and Beyond
As retatrutide research continues to evolve, emerging data and novel applications are shaping dosing strategies and expanding our understanding of optimal protocols.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Multiple phase 2 and phase 3 trials are currently investigating retatrutide across various applications:
- Extended duration studies: Evaluating 2+ year outcomes and safety profiles
- Comparative trials: Head-to-head studies against tirzepatide and semaglutide
- Combination approaches: Retatrutide with complementary interventions
- Special populations: Pediatric, geriatric, and specific disease state research
- Cardiovascular outcomes: Long-term impact on cardiovascular events
These studies will likely refine dosing recommendations and identify population-specific optimization strategies.
Personalized Dosing Approaches
Emerging research explores individualized dosing based on:
🧬 Genetic factors: Receptor polymorphisms affecting response
🧬 Metabolic phenotyping: Baseline metabolic characteristics predicting optimal doses
🧬 Biomarker-guided titration: Using specific markers to guide dose escalation
🧬 Machine learning models: Predictive algorithms for dose optimization
These personalized approaches may eventually replace one-size-fits-all protocols with tailored strategies.
Novel Administration Routes
While subcutaneous injection remains standard, research is exploring:
- Oral formulations: Overcoming peptide stability challenges
- Transdermal delivery: Patch-based administration systems
- Extended-release formulations: Bi-weekly or monthly dosing options
- Combination products: Fixed-dose combinations with complementary compounds
These innovations could significantly alter dosing paradigms if proven effective.
Expanding Applications
Beyond metabolic research, retatrutide shows promise in:
- Cardiovascular disease: Direct cardioprotective effects independent of weight loss
- Fatty liver disease: NASH/NAFLD treatment applications
- Neurodegenerative conditions: Potential neuroprotective properties
- Inflammatory disorders: Anti-inflammatory mechanisms
- Aging research: Metabolic optimization and longevity studies
These diverse applications may require modified dosing strategies optimized for specific outcomes.
Conclusion: Establishing Your Retatrutide Research Protocol
Determining what’s the right starting dose for retatrutide requires careful integration of evidence-based guidelines, individual subject characteristics, specific research objectives, and comprehensive safety monitoring. The preponderance of current evidence supports 1-2 mg weekly as the optimal starting point for most research applications, with methodical 4-week escalation to maintenance doses of 8-12 mg weekly.
This conservative, step-wise approach maximizes both scientific validity and subject safety by:
- Minimizing adverse gastrointestinal reactions during initial exposure
- Allowing proper assessment of individual tolerance patterns
- Providing flexibility for protocol adjustments based on observed responses
- Maintaining research continuity through reduced discontinuation rates
- Achieving comparable long-term efficacy to more aggressive dosing strategies
Key Implementation Steps:
- Establish comprehensive eligibility criteria based on BMI, metabolic status, and health parameters
- Conduct thorough baseline assessments including laboratory work, physical measurements, and medical history
- Initiate dosing at 1-2 mg weekly for 2-4 weeks, monitoring closely for adverse reactions
- Follow evidence-based titration schedule, escalating every 4 weeks unless tolerability concerns emerge
- Maintain flexible protocols that allow extended duration at current doses when needed
- Implement robust safety monitoring with regular assessments and clear stopping criteria
- Source high-purity research peptides from reputable suppliers with comprehensive documentation
- Document meticulously to ensure research integrity and regulatory compliance
For research facilities seeking to establish retatrutide protocols, partnering with reliable peptide suppliers ensures access to research-grade compounds with verified purity and appropriate documentation. PEPTIDE PRO delivers high-purity research peptides with fast UK delivery, comprehensive product information, and professional customer support—trusted by researchers and laboratories across the UK and worldwide.
Ready to advance your metabolic research? Explore research-grade retatrutide options and access the quality, consistency, and service your protocols demand. For questions about specific research applications, reconstitution protocols, or product availability, contact our research support team for expert guidance.
References
[1] Phase 2 clinical trial data comparing 2 mg vs. 4 mg starting doses, demonstrating reduced gastrointestinal adverse events with lower initial dosing (Eli Lilly and Company, 2023)
[2] Jastreboff AM, et al. “Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity — A Phase 2 Trial.” New England Journal of Medicine, 2023; 389:514-526
[3] 48-week efficacy data from phase 2 dose-ranging trials showing up to 24% body-weight reduction at optimal maintenance dosing (Clinical trial NCT04881760, 2023)
